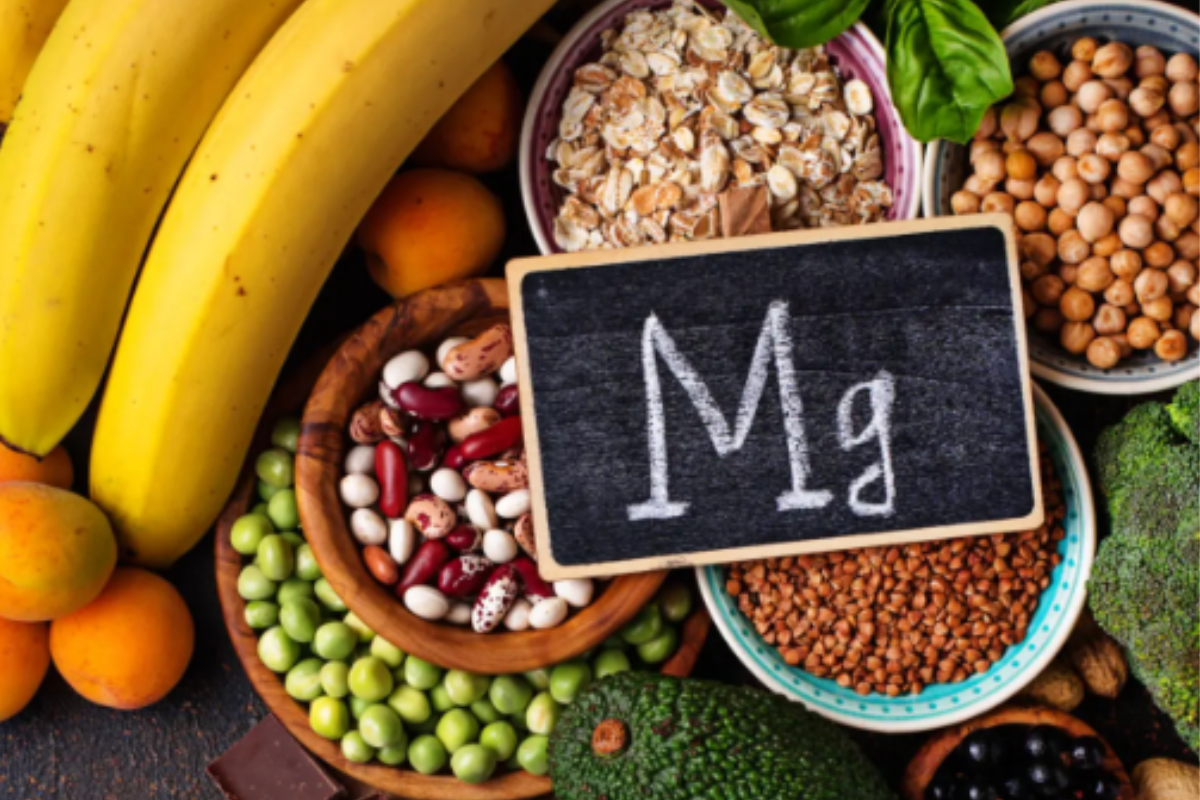
The Importance of Magnesium for Energy Production and Relaxation
The Importance of Magnesium for Energy Production and Relaxation
It is among the most vital minerals in the body and plays a role in more than 300 reactions. While magnesium is an essential nutrient that is present in human physiology and is so evidently necessary to human health, magnesium is often overlooked, as are other important nutrients. Magnesium plays a vital role in guaranteeing that our body works suitably — from energy production to muscle function, even to sleep regulation. In this article, we will talk about the part of magnesium in energy production and muscle relaxation, in addition to its importance for overall health, magnesium-rich foods, and magnesium supplements.
Magnesium plays an essential role in metabolism as it is required for energy production.
It is essential for energy metabolism. Magnesium supports the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the cellular energy currency. ATP fuels almost every cell function, from muscle contraction to nerve signalling. A deficiency causes a burden on the body that is unable to produce sufficient ATP; the body feels tired and lethargic. Ensuring you have enough magnesium in your diet will assist with your internal energy generation processes and prevent you from being sluggish during your day.
Magnesium also regulates blood sugar. It encourages insulin to work correctly, which helps stabilize blood sugar levels. That is significant, as it keeps you far off from those blood sugar highs and lows that usually follow a few hours later. Magnesium helps ensure that your body can utilize glucose (sugar) for energy, and having energy to get through your day is very important.
Magnesium for Relaxed Muscling and Functioning
Besides being involved in energy production, muscles require magnesium to function normally. It regulates calcium homeostasis in muscle cells, which controls muscle contractions. Magnesium is the mineral that relaxes muscles; therefore, the muscles will contract too hard due to the lack of magnesium, which causes cramps and spasms. Magnesium likewise loosens up the muscle strands, and it additionally stops muscle strands from fixing, which can help prevent muscle spasms, particularly after activity.
Magnesium is also a relaxant. It acts as a natural muscle relaxer, easing physical tension and discomfort. It can be beneficial for someone with chronic tight muscles (a collection of discomfort conditions, tension headaches, or fibromyalgia). Magnesium is helpful for athletes or individuals who perform intense exercise as it aids in muscle relaxation and the recovery process after exercise, easing muscle soreness.
The Role of Magnesium in Sleep & relaxation
One of those less out there, but arguably just as essential, functions that magnesium provides is to sleep well at night. Melatonin is your body's night-time hormone, and magnesium helps regulate its secretion and lets you fall asleep faster. It also attaches to GABA receptors that calm the nervous system and promote relaxation. Some studies have, therefore, found magnesium to aid in getting healthy sleep and preventing insomnia.
Magnesium is a non-addictive way for anyone to get caught up on sleep and get sleep times back on track after insomnia-related sleep disorders or anxiety situations. It can help restore broken sleep cycles. Having magnesium before sleep might quieten a racing brain, resulting in deeper and more refreshing sleep.
Magnesium-rich Foods: How to Get More?
However, magnesium never arrives on a prescription pad, and that's where you come into play: you infiltrate their bios tent and forge an association between them and a magnesium-rich chow group. Top sources of magnesium-rich foods are greens like spinach and kale, nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds (pumpkin, sunflower), whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, black beans, and lentils. Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel are also among the best sources of magnesium.
In addition to magnesium-rich foods, there are magnesium supplements that are perfect for those who are no longer magnesium meals. Before testing for deficiencies and starting a supplement, however, a person should speak to a doctor. They can help decide the proper amount and confirm magnesium supplements will not negatively react with other drugs or conditions.
Pros of Added Magnesium
While eating more magnesium-rich foods should be your number-one priority, supplements are beneficial for people who are deficient or at risk of deficiency. There are various types of magnesium supplements, such as magnesium citrate, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium oxide. Each type has different absorption rates and benefits, so choosing the right kind is proper for your use.
This is why you should always consult with your healthcare provider before starting supplementation to ensure that what you are taking is sufficient dosage. High magnesium from supplements may cause diarrhoea, nausea, or stomach cramps. Everybody needs to find their sweet spot.
Conclusion: How Magnesium Instantly Supports Energy & Relaxation
Impact you will get: Magnesium is considered to be one of the most functional minerals inside the body for many mobile aspects like energy, muscle relaxation, and sleep. Making sure to eat enough magnesium is one of the most effective ways you can improve your health. Consuming magnesium-rich foods, in addition to supplementation, when necessary, will promote energy, muscle function, and sleep. Talk to your doctor about how much magnesium you need in order to maximize and marvel at the health magics of magnesium!





















































