Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health Affecting Mental Health

Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health Affecting Mental Health
Introduction
The intricate relationship between our gut and our brain, often referred to as the "gut-brain axis," has been a growing area of scientific interest. Research suggests that the health of our digestive system can significantly impact our mental well-being. This blog post will explore the fascinating connection between lifestyle factors, gut health, and mental health, providing insights into how we can optimize our overall well-being.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Complex Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that involves the nervous system, hormones, and the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome, consisting of trillions of microorganisms, plays a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and the production of neurotransmitters.
Research has shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome, often referred to as dysbiosis, can have far-reaching consequences for mental health. These imbalances can be influenced by various lifestyle factors, including diet, stress, and medication use.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Gut Health and Mental Health
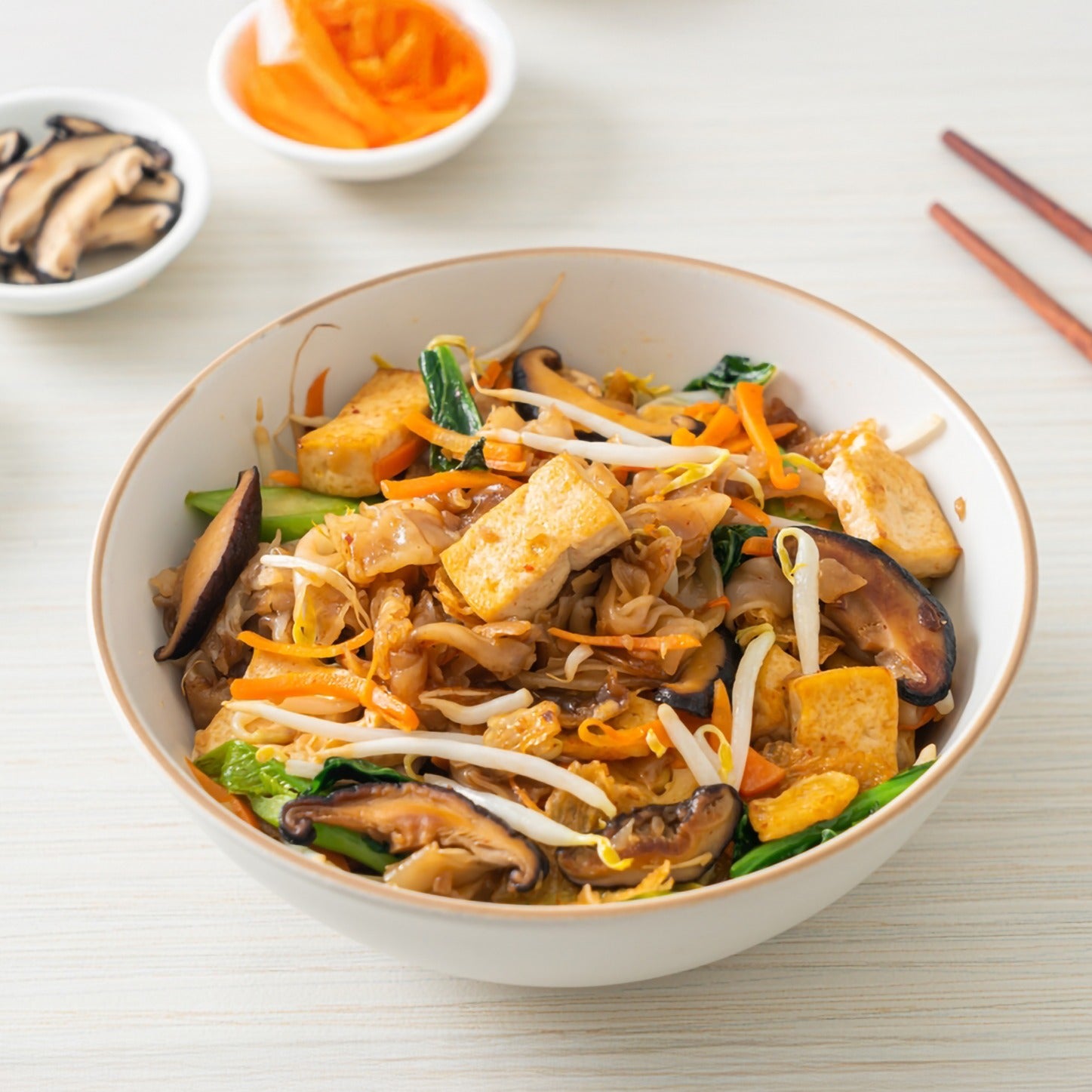
- Diet: To support a healthy gut microbiome, incorporate probiotic and Fiber-Rich Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into your diet. Limit your intake of processed foods, which can disrupt gut health. also Pay attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues and avoid eating when stressed or distracted.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health and contribute to mental health issues. To manage stress and support overall well-being, practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga.
- Exercise: Regular Physical Exercise has been shown to improve both physical and mental health. It can also positively influence gut health.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall well-being, including mental health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Medication Use: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiome. Consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
- Probiotics and Supplements: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that probiotics and certain supplements may support gut health and mental well-being. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Mental Health
- Neurotransmitter Production: The gut microbiome plays a role in producing neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for mood regulation and cognitive function.
- Inflammation: Imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to inflammation, which has been linked to various mental health conditions.
- Immune Function: The gut microbiome interacts with the immune system, and disruptions in this interaction may affect mental health.
Conclusion
The connection between lifestyle factors, gut health, and mental health is becoming increasingly evident. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, supporting gut health, and addressing underlying issues, individuals can significantly improve their overall well-being. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.





















































